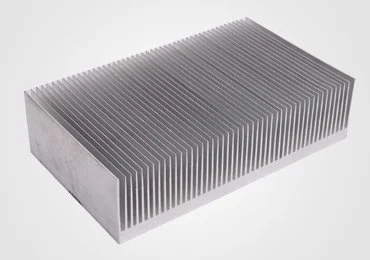
Custom Heat Sink-Pin Fin Heat Sink
Enhanced Cooling with Pin Fin Heat Sinks: Efficient Heat Dissipation for Electronics
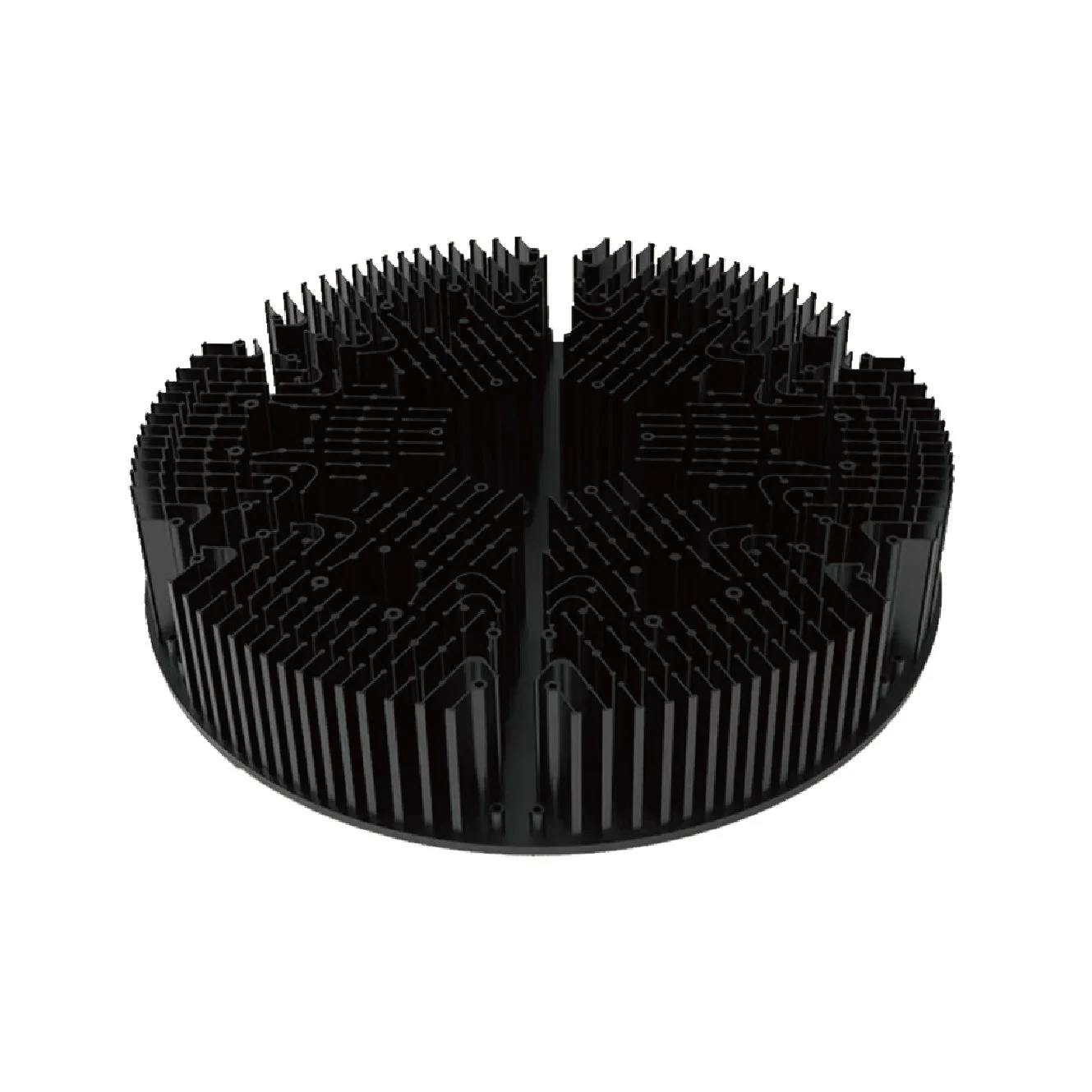
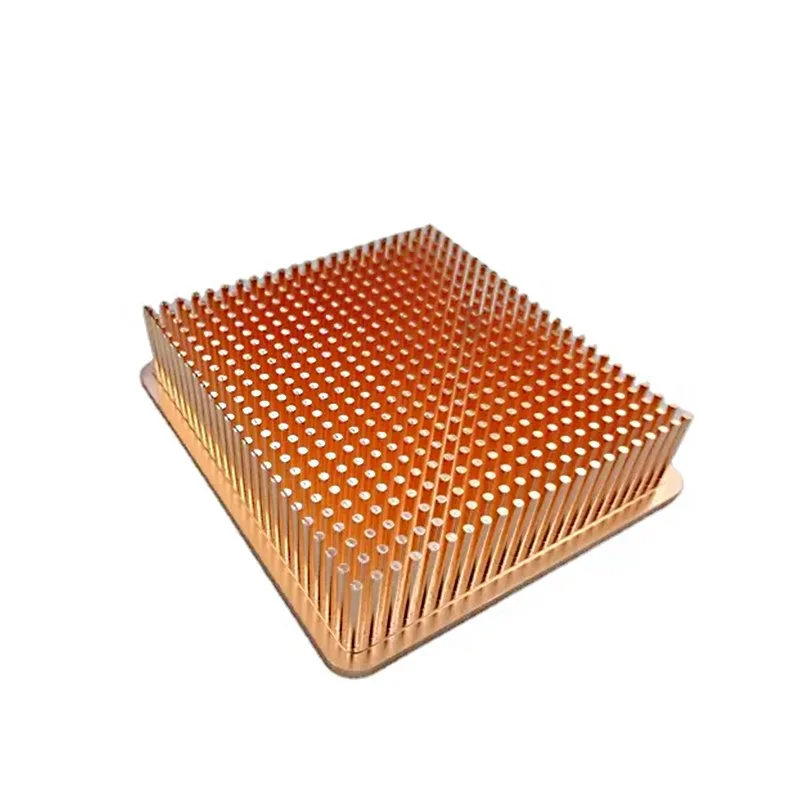
A pin fin heat sink is a cooling device with many small, closely spaced pins or fins. It's used to cool hot components by increasing the surface area for better heat dissipation. Heat travels from the component into the base of the heat sink, then into the fins. Air flowing around the fins carries away the heat, preventing overheating. These heat sinks are valuable in compact spaces and are used in electronics, vehicles, and more. Our pin fin heatsinks offer customization options to suit your requirements. If you possess a unique design and layout in mind, we are here to assist you in perfecting the concept for its eventual manufacturing.
Basic Info About Our Pin Fin Heat Sinks
| Material | Aluminum Alloy 6000 Series |
| Base Thickness | Based on your requirements. |
| Pin Height | Based on your requirements. |
| Shapes | Square, square, round, or customized |
| Application | Electronics/LED Lighting/Automotive Electronics/Telecommunications/Industrial Equipment/Inverter,/Welding Machine/Power Supply Equipment/Thermoelectric Coolers/Generator, IGBT/UPS Cooling Systems, etc. |
| Finish | Anodizing, Mill finish, Electroplating, Polishing, Sandblasted, Powder coating, Silver plating, Brushed, Painted, PVDF, etc. |
| Deep process | CNC,drilling,milling,cutting,stamping,welding,bending,assembling,Custom Aluminum Fabrication |
| MOQ | Low MOQ |
| Packaging | standard export packaging or as discussed |
| Certificate | CE/SGS/ISO/Rohs |
| Service | 1. Free sample, Free design. 2. OEM/ODM available. 3. Custom-made request. 4. New design solution suggestion. |
| Delivery time | 15-20 days after sample confirmed & done payment, or negotiated |
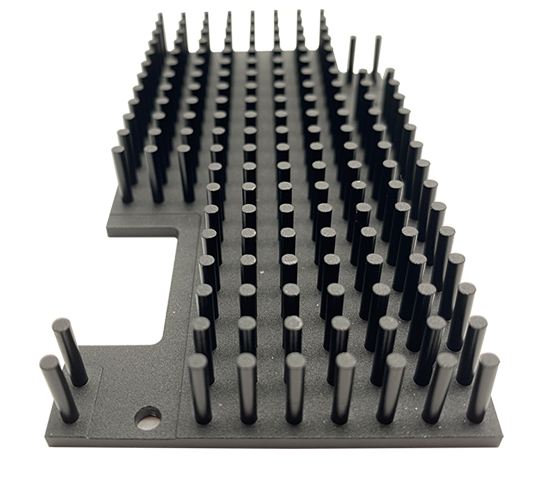
Some Size Display
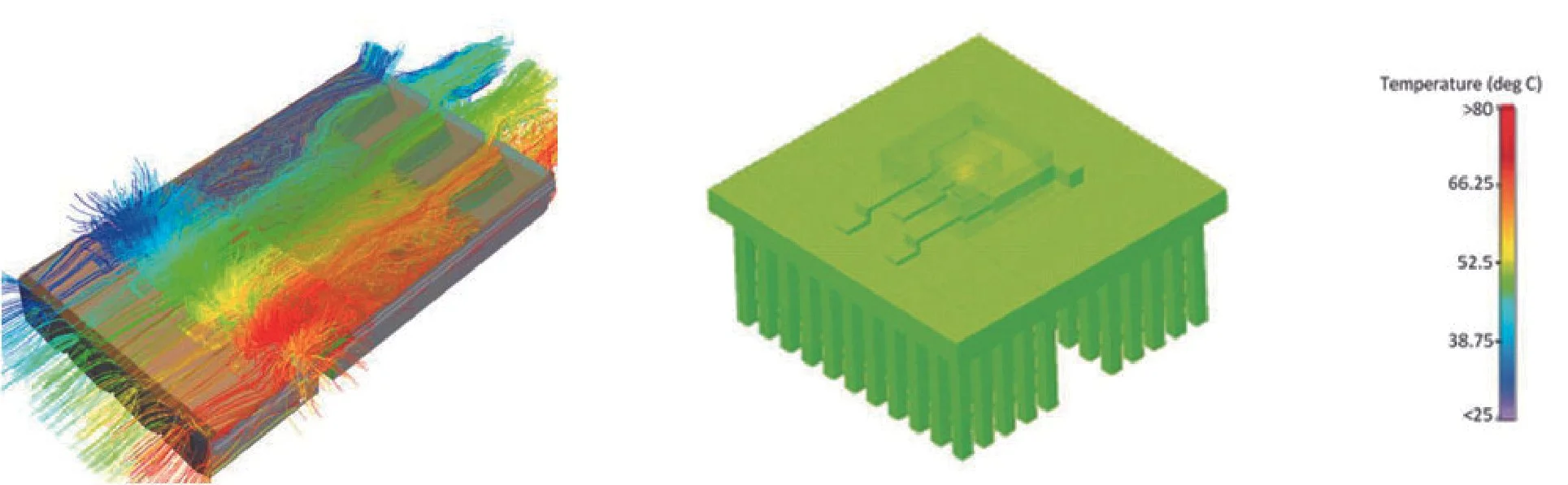
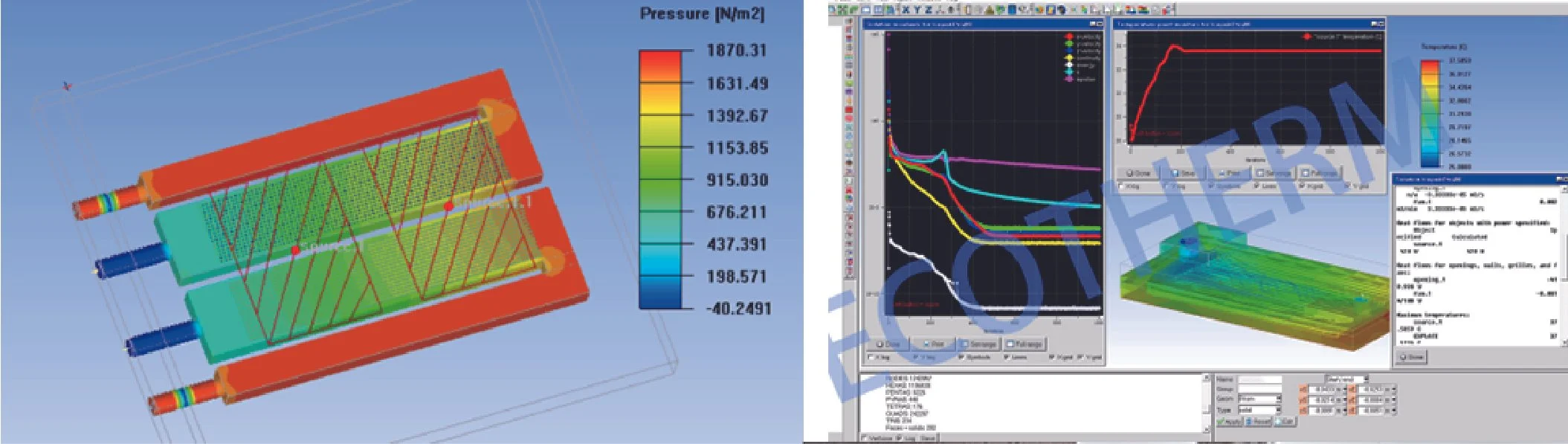
Thermal Design&Thermal Simulation
Our Workshop
Our Common Products
Part of Products
● Efficient Cooling in Vertical Orientation
● Aesthetic Appeal
● Versatility
● Improved Structural Integrity
send 3D and CAD drawing, confirm production details
confirm the order and start to make samples.
Customization Process
surface treatment confirmation.
send samples to confirm quality and product details
we send the quotation to your for review.
after sample is confirmed, we will start mass production
The Process of Heat Sink Production
Products You May Looking for
zipper fin heat sink
heat pipe heat sink
stamping heat sink
die cast heat sink
stacked fin heat sink
Our Packaging
Advantages of pin fin heat sinks
● High Surface Area: The numerous pins or fins provide a larger surface area compared to traditional heat sinks, allowing for improved heat dissipation and more efficient cooling.
● Effective Heat Transfer: The increased surface area enhances convection, enabling faster and more effective heat transfer from the source to the surrounding air.
● Compact Design: The closely spaced pins result in a compact and space-efficient heat sink, making it suitable for applications with limited room for cooling solutions.
● Customizability: Pin fin heat sinks can be tailored to specific requirements, allowing for adjustments in pin height, density, and arrangement to optimize thermal performance for different components and applications.
● Versatility: They are versatile and can be used in various industries and applications, from electronics to automotive to industrial equipment.
● Improved Cooling in Restricted Spaces: The compact design of pin fin heat sinks makes them particularly useful in situations where other cooling solutions might not fit or be as effective.
● Reduced Thermal Resistance: The efficient heat transfer capabilities of pin fin heat sinks help in reducing the thermal resistance between the heated component and the ambient environment.
● Higher Cooling Efficiency: Their enhanced heat dissipation ability enables these heat sinks to efficiently manage heat even in high-power applications, preventing overheating.
● Enhanced System Reliability: By keeping components within safe temperature limits, pin fin heat sinks contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of electronic and mechanical systems.
● Aesthetic Considerations: The design of pin fin heat sinks can also contribute to the aesthetics of the device, as they can be shaped and designed to match the overall product appearance.
Pin fin heat sinks are widely applied across industries to efficiently dissipate heat. They find use in electronics like computers and servers, cooling components such as CPUs and GPUs, while also extending LED lifespan. In vehicles, they cool automotive electronics like ECUs and batteries, and in telecommunications, they manage heat in networking equipment. Industrial machinery benefits from them in motor drives and power inverters. Renewable energy systems utilize them in solar inverters and wind turbine electronics. Additionally, they're crucial in medical devices, consumer electronics, aerospace electronics, HVAC systems, and power electronics, ensuring reliable operation and preventing overheating in applications ranging from sensitive medical equipment to entertainment systems to avionics.
Application Display
Application of pin fin heat sinks
Among the array of available heat sink technologies, our pin fin heat sinks shine as an exceptionally effective cooling solution. Their distinguishing feature lies in the ample surface area they provide relative to their compact volume. With pin spacing and round pins characterizing our Tone pin fin heat sinks, their construction from high thermal conductivity materials like copper or aluminum alloys ensures an elevated convective thermal efficiency.
Furthermore, our pin fin heat sinks boast superior volumetric efficiency, rendering them remarkably lighter and more compact than their cooling prowess would suggest. Impressively, they outperform extrusion heat sinks by 2 to 10 times in efficiency.
Notably absent in our pin fin heat sinks are bonding agents, thereby allowing for a range of plating methods. This translates to versatile options such as anodization or oxidation, depending on the chosen material. Their robustness equips them to thrive in demanding industrial or commercial environments, making them a dependable choice.
Whether you are a supplier or a distributor, we are well-equipped to fulfill your needs. Our commitment extends to offering round-the-clock customer service, ensuring that your inquiries and concerns are promptly addressed.
keep reading to learn more about extruded heat sink
What is Pin Fin Heat Sink
A pin fin heat sink is a specialized cooling component designed to dissipate heat efficiently from electronic devices, mechanical systems, or other equipment that generates excess heat during operation. It consists of an array of small, closely spaced pins or fins that extend from a base or plate. These fins are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, to facilitate effective heat transfer.
When attached to a heat-generating component, such as a microprocessor or power transistor, the heat is conducted through the base of the heat sink and then into the fins. As air circulates around the pins, heat is transferred from the fins to the air through convection, effectively lowering the temperature of the component and preventing overheating.
Pin fin heat sinks are particularly advantageous in applications with limited space, as their compact design offers superior heat dissipation in confined areas. Their enhanced surface area allows for improved convective heat transfer, making them a popular choice for various industries, including electronics, automotive, aerospace, and more.
● High Surface Area: The arrangement of closely spaced pins provides a larger surface area compared to traditional heat sinks, resulting in more efficient heat transfer and better cooling performance.
● Efficient Heat Dissipation: The increased surface area enables quicker and more effective heat dissipation through convection, ensuring that components remain within safe temperature ranges.
● Compact Design: Pin heat sinks are compact and space-efficient, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or unconventional cooling solutions are required.
● Customizable: The number, height, and arrangement of the pins can be customized to suit specific thermal requirements, allowing for optimized cooling solutions tailored to different components or devices.
● Versatility: They find application in various industries, including electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and aerospace, due to their adaptability and effectiveness in diverse environments.
● Improved Thermal Performance: Pin heat sinks can efficiently manage heat generated by high-power components, preventing overheating and potential performance degradation.
● Enhanced Airflow: The closely spaced pins help guide and channel airflow, increasing the efficiency of heat transfer and convective cooling.
● Reduced Thermal Resistance: The efficient heat dissipation properties of pin heat sinks result in lower thermal resistance, allowing for improved heat flow from the source to the surrounding environment.
● Reliability and Longevity: By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, pin heat sinks contribute to the overall reliability and lifespan of components and systems.
● Aesthetic Considerations: The design of pin heat sinks can also contribute to the overall aesthetics of a device or equipment, blending functionality with visual appeal.
● Environmentally Friendly: The absence of bonding agents and the potential for plating methods make pin heat sinks suitable for various surface treatments, contributing to their adaptability and eco-friendliness.
Benefits of Pin Heat Sink
Pin fin heat sinks are commonly made from materials with high thermal conductivity to ensure efficient heat transfer and dissipation. The two most frequently used materials for pin fin heat sinks are aluminum and copper:
Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight and cost-effective material with decent thermal conductivity. It's widely used for pin fin heat sinks due to its availability and suitability for many applications. Aluminum heat sinks are often extruded, machined, or stamped into the desired pin fin shape.
Copper: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity, significantly better than aluminum. This makes copper an optimal choice for applications that demand enhanced heat transfer capabilities. Copper pin fin heat sinks are particularly suitable for high-performance applications and situations where heat dissipation is critical.
The material selection often depends on factors such as the specific thermal requirements of the application, budget considerations, weight constraints, and design preferences. Both aluminum and copper have their advantages, and the choice of material will depend on the balance of these factors in a particular application.
Bimetal: This composite material ingeniously melds the qualities of copper and aluminum, resulting in an exceptionally potent hybrid compound. It not only offers reduced weight but also boasts remarkable corrosion resistance to coolants, all without necessitating surface plating. This amalgamation ensures superb heat distribution and the ability to rapidly absorb short-duration peak loads.
Material of Pin Fink Heat Sink
Manufacturing pin fin heat sinks involves several processes to create the intricate design and optimize their heat dissipation capabilities.
● Material Selection: Choose a suitable material with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum, copper, or bimetal (a combination of copper and aluminum). The material choice affects both performance and cost.
● Extrusion or Machining: For aluminum or copper heat sinks, extrusion is a common method. In this process, the material is heated and forced through a die to create the desired cross-sectional shape. Alternatively, machining can be used to remove material and shape the fins from a solid block.
● Design and Layout: Determine the layout and arrangement of the pins or fins based on the application's thermal requirements. Factors such as pin density, height, and spacing are crucial for effective heat dissipation.
● Cutting and Forming: The extruded or machined pieces are cut into appropriate lengths, and the pin fins are formed through bending or other shaping techniques. This step establishes the three-dimensional structure of the heat sink.
● Surface Finishing: Apply surface treatments to enhance thermal performance and protect against corrosion. Anodization, painting, or other coatings might be added for aesthetic or functional purposes.
● Quality Control: Inspect the heat sinks for dimensional accuracy, surface finish quality, and any defects that could impact performance. This step ensures that the manufactured heat sinks meet the desired specifications.
● Testing: Conduct thermal testing to verify the heat sink's performance under different conditions. This may involve measuring temperature differences, heat transfer rates, and overall cooling efficiency.
● Customization: Depending on the application, some heat sinks might require further customization, such as additional features or modifications to match specific components.
● Assembly: If required, attach the heat sink to the heat-generating component using appropriate thermal interface materials like thermal paste or thermal pads.
● Installation: Install the assembled heat sink within the intended device or system, ensuring proper positioning and alignment.
Fabricating Pin Fin Heat Sink
● Conduction: The heat generated by the electronic component, such as a CPU or power transistor, is transferred to the base of the pin fin heat sink through direct contact. The base of the heat sink is designed to have good thermal conductivity, allowing heat to flow from the hot component to the heat sink.
● Convection: Once the heat is transferred to the base of the heat sink, it travels through the pins or fins. These pins are closely spaced and have a high surface area, which facilitates efficient heat dissipation through convection. As air flows around the pins due to natural convection (or forced convection from a fan), heat is transferred from the fins to the air.
● Heat Transfer: The heat transfer process occurs as follows: -Heat flows from the component into the heat sink's base. -From the base, heat travels through the pins or fins due to their thermal conductivity. -Air circulating around the pins absorbs the heat, leading to a temperature decrease in the heat sink and, consequently, in the component attached to it. -Cooling Effect: The continuous flow of air and the increased surface area of the pins result in efficient cooling. As the heat is transferred from the component to the heat sink and then to the surrounding air, the component's temperature remains within safe operating limits.
● Temperature Regulation: The pin fin heat sink maintains a balance between the heat generated by the component and the heat dissipated into the environment. This prevents the component from overheating, which could lead to performance degradation or even failure.
The design and effectiveness of a pin fin heat sink depend on factors like pin density, arrangement, material conductivity, airflow rate, and overall system configuration. By optimizing these parameters, pin fin heat sinks provide a compact and effective solution for managing thermal issues in various applications, ensuring reliable operation and extending the lifespan of electronic devices and systems.
How Pin Fin Heat Sink Works
Categorized by airflow dynamics, pin fin heat sinks come in both passive and active variants. In the active configuration, a powered element such as a fan or blower is positioned in proximity to the heat exchanger surface. This arrangement leverages forced airflow to efficiently channel air over the fin area. Conversely, passive pin fin heat sinks depend less on compelled airflow, often praised for their reliability over active alternatives.
Segmented by material, pin fin heat sinks are available in aluminum and copper variations. These nomenclatures concisely indicate the composition used in crafting each type.
In terms of manufacturing processes, several types of this heat sink are prevalent. Among these, notable options encompass CNC-machined pin fin heat sinks, among others.
Within the domain of water-cooled solutions, key varieties of this heat sink include solid metal pin fin heat sinks, pumped liquid pin fin heat sinks, and two-phase pin fin heat sinks.
Types of Pin Fin Heat Sink
Pin fin heat sinks and skived fin heat sinks are distinct cooling solutions with differing designs and applications. Pin fin heat sinks feature closely spaced pins extending from a base, providing high surface area for efficient heat dissipation, making them suitable for moderate to high heat loads. Skived fin heat sinks, created by machining folded fins from solid metal blocks, induce turbulence in airflow, enhancing convection and making them efficient for moderate heat loads. While pin fin heat sinks offer more customization and are generally more efficient, skived fin heat sinks can be advantageous in space-constrained scenarios due to their folded design. The choice between the two depends on factors like heat load, available space, and application-specific requirements.
pin heat sink
skived fin heat sink
Pin Fin Heat Sink vs Skived Fin Heat Sink
Selecting the appropriate pin fin heat sink for any application involves a comprehensive assessment of factors such as the heat load generated by the component, available space for installation, pin density and arrangement, optimal material (aluminum or copper), customization potential, airflow conditions, cooling environment, industry-specific needs, performance metrics, manufacturing quality, budget constraints, reliability considerations, and testing or simulation results. By diligently considering these aspects, a well-informed choice can be made to ensure efficient thermal management and optimal system performance.
a) Opt for a pin fin heat sink when your application necessitates natural convection cooling and specific orientations.
b) Consider a pin fin heat sink if substantial pressure drops across the heat sink still allow reasonable airflow rates, making it a suitable choice.
c) When dealing with an uncertain airflow direction in a forced convection-cooled heat sink, using a pin fin heat sink is recommended, as it exhibits reduced sensitivity to flow direction. In summary, unless your scenario falls within the categories mentioned above, a plate-fin heat sink is advisable for other applications.